When molecules move from higher to lower concentration what do we call that?
Improvidence and Osmosis
- Page ID
- 23851
one. Description of Diffusion and Osmosis
A water solution that contains nutrients, wastes, gases, salts and other substances surrounds cells. This is theexternal environment of a cell. The jail cell's outer surface of the plasma membrane is in contact with this external surroundings, while the inner surface is in contact with the cytoplasm. Thus, the plasma membrane controls what enters and leaves the jail cell.
The membrane permits the passage of some materials, but not all. The jail cell membrane is said to beselectively permeable. Minor molecules, for example, may laissez passer through the membrane. If no energy is required for substances to laissez passer through the membrane, the procedure is calledpassive transport. We volition discuss 2 examples of passive send in this tutorial:diffusion andosmosis.
Diffusion
Although you may non know what diffusion is, you accept experienced the procedure. Can you remember walking into the front door of your home and smelling a pleasant olfactory property coming from the kitchen? It was diffusion of molecules from the kitchen to the front door of the business firm that immune you to detect the odors.
Improvidence is defined as the cyberspace move of molecules from an surface area of greater concentration to an area of bottom concentration.
The molecules in a gas, a liquid or a solid are in constant movement due to theirkinetic energy. Molecules are in constant movement and collide with each other. These collisions crusade the molecules to movement in random directions. Over time, however, more molecules will exist propelled into the less concentrated area. Thus, the net motility of molecules is always from more than tightly packed areas to less tightly packed areas. Many things can diffuse. Odors diffuse through the air, salt diffuses through water and nutrients diffuse from the claret to the torso tissues.
This spread of particles through random motion from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration is known as diffusion. This unequal distribution of molecules is called aconcentration gradient. Once the molecules get uniformly distributed,dynamic equilibriumexists. The equilibrium is said to be dynamic because molecules continue to move, but despite this change, there is no net change in concentration over time. Both living and nonliving systems experience the process of diffusion. In living systems, improvidence is responsible for the movement of a big number of substances, such as gases and small uncharged molecules, into and out of cells.
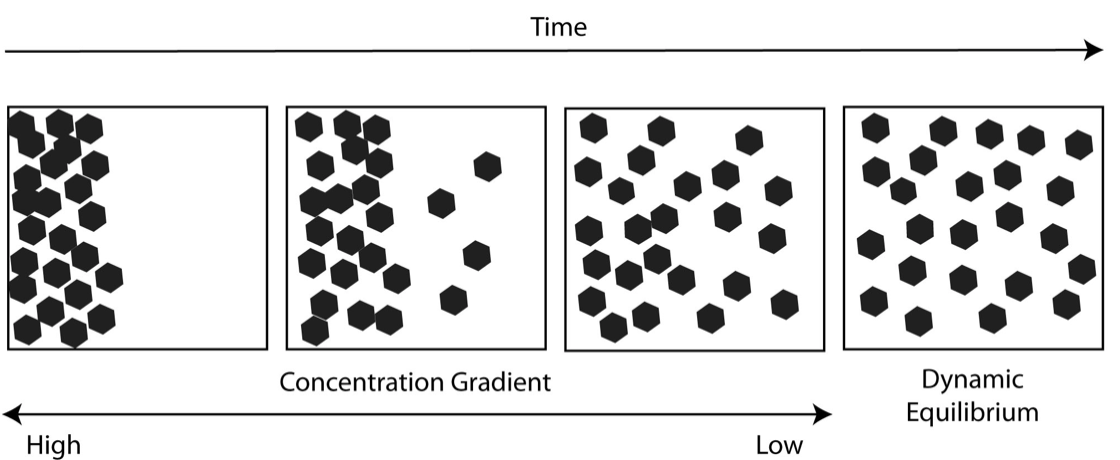
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\). (CC BY-NC-SA)
Osmosis
Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion; it is the passage of water from a region of high water concentration through a semi-permeable membrane to a region of depression water concentration.
Semi-permeable membranes are very thin layers of textile which let some things to laissez passer through them, but foreclose other things from passing through. Cell membranes are an instance of semi-permeable membranes. Cell membranes allow small-scale molecules such as oxygen, water carbon dioxide and glucose to laissez passer through, but do not permit larger molecules similar sucrose, proteins and starch to enter the cell directly.
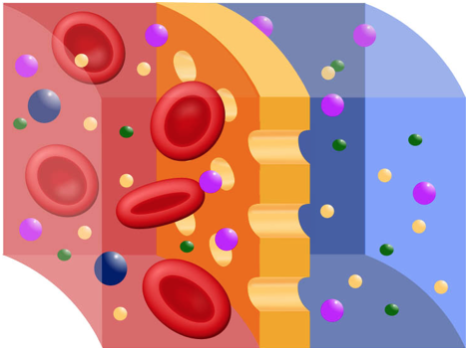
Figure \(\PageIndex{ii}\). (CC Past-NC-SA)
Example: If at that place was a semi-permeable membrane with more water molecules on i side as there were on the other, h2o molecules would period from the side with a loftier concentration of water to the side with the lower concentration of water. This would keep until the concentration of water on both sides of the membrane were equal (dynamic equilibrium is established).
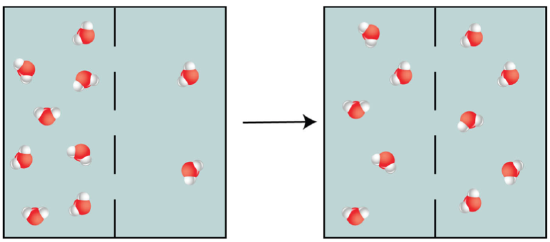
Figure \(\PageIndex{three}\). (CC By-NC-SA)
Osmotic Pressure
Calculation sugars to h2o volition result in a subtract in the water concentration because the saccharide molecules displace the water molecules.
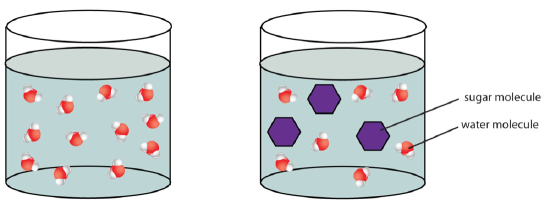
Effigy \(\PageIndex{four}\). osmotic pressure (CC BY-NC-SA;LadyOfHats)
If the ii containers are connected, only separated by a semi-permeable membrane, h2o molecules would catamenia from the area of loftier water concentration (the solution that does not incorporate whatsoever saccharide) to the area of lower h2o concentration (the solution that contains sugar).
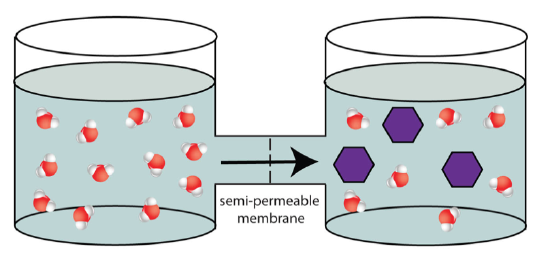
Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\). osmotic pressure (CC Past-NC-SA;LadyOfHats)
This movement of water would continue until the water concentration on both sides of the membrane is equal, and will effect in a modify in volume of the two sides. The side that contains sugar will stop upwards with a larger volume.
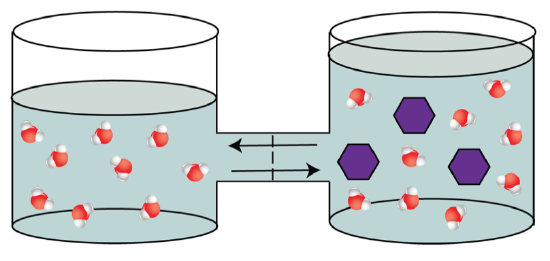
Figure \(\PageIndex{vi}\). osmotic pressure (CC Past-NC-SA;LadyOfHats)
Water solutions are very important in biology. When water is mixed with other molecules this mixture is called asolution. Water is thesolvent and the dissolved substance is thesolute. A solution is characterized by the solute. For example, h2o and sugar would exist characterized every bit a sugar solution.
The classic case used to demonstrate osmosis and osmotic pressure level is to immerse red blood cells into saccharide solutions of various concentrations. There are three possible relationships that cells can encounter when placed into a sugar solution.
one. The concentration of solute in the solution tin beequal to the concentration of solute in cells. In this situation the cell is in anisotonic solution (iso = equal or the same as normal). A red blood cell will retain its normal shape in this environment as the amount of water entering the prison cell is the same as the corporeality leaving the prison cell.
2. The concentration of solute in the solution can begreater than the concentration of solute in the cells. This prison cell is described as being in ahypertonic solution (hyper = greater than normal). In this situation, a red blood will announced to shrink as the water flows out of the cell and into the surrounding environment.
iii. The concentration of solute in the solution can beless than the concentration of solute in the cells. This jail cell is in ahypotonic solution (hypo = less than normal). A red claret prison cell in this environment will become visibly swollen and potentially rupture as water rushes into the prison cell.
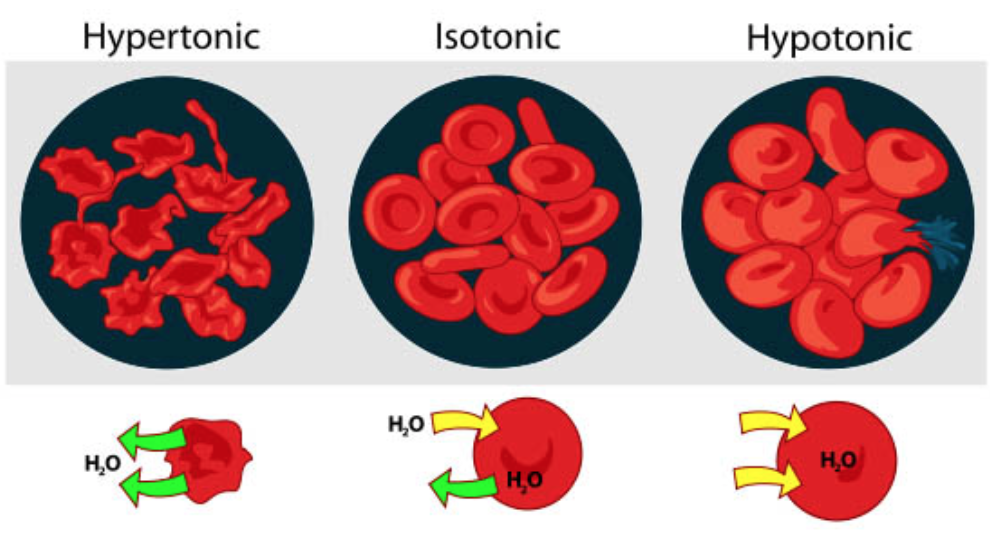
Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\). (CC BY-NC-SA)
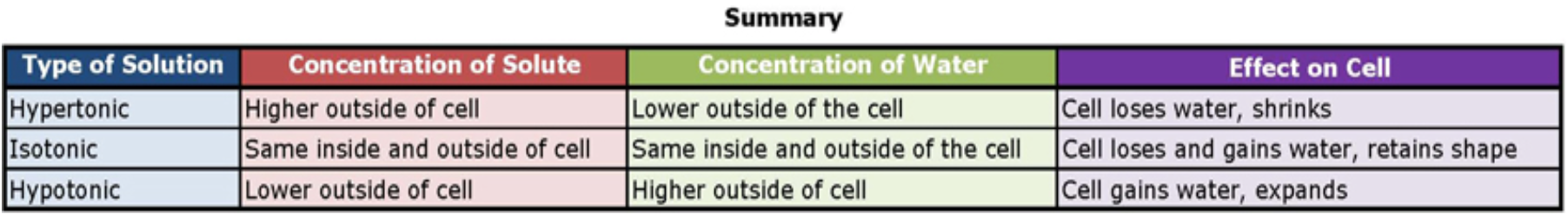
Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\). (CC Past-NC-SA)
Source: https://bio.libretexts.org/Learning_Objects/Worksheets/Biology_Tutorials/Diffusion_and_Osmosis
0 Response to "When molecules move from higher to lower concentration what do we call that?"
Post a Comment